These identifiers are meant for identifying devices within a network, they have different roles and importance for safety. Hence, knowing a difference between MAC address vs IP address can be critical.
Understanding these two parameters is key for anyone interested in cybersecurity, digital marketing work or simply managing their own devices more effectively.
What is a MAC Address?
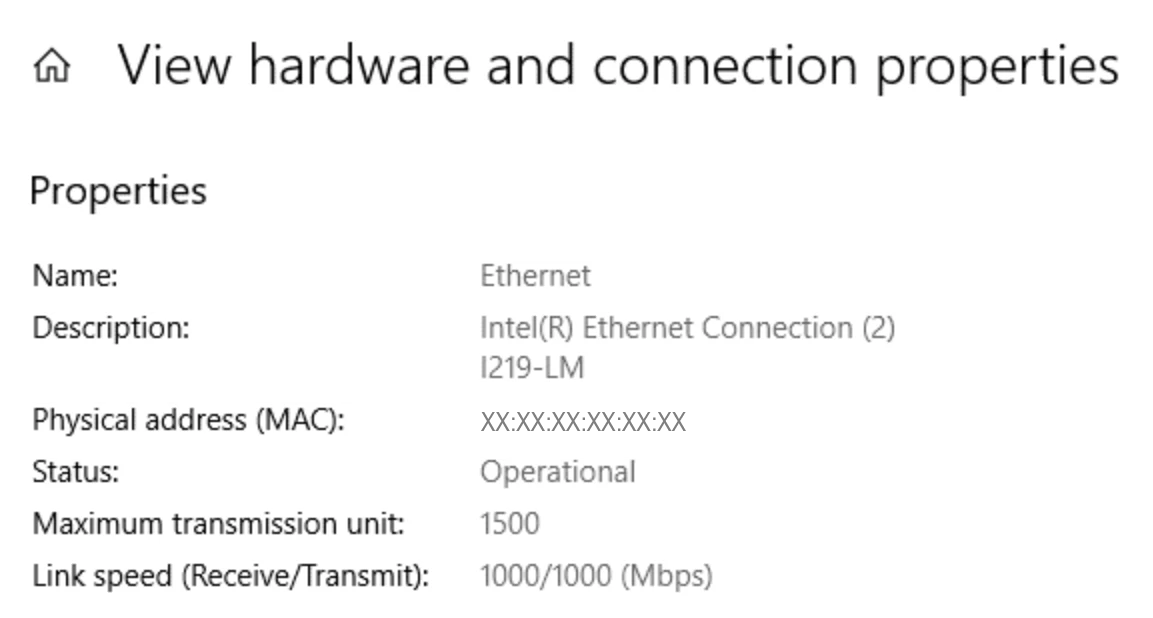
A MAC (Media Access Control) address is comparable to an ID card for a network card in a device. It serves as a kind of permanent device ID for devices on a local network to recognize each other.
Whether you are using a laptop, mobile phone or printer, each of these devices has its own MAC address – and this code does not change, regardless of which Wi-Fi network the hardware is connecting to.
Structure and Format
A MAC address operates 48 bits and is typically represented as a string of 12 digits, such as 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E. It consists of two sections:
- Manufacturer ID: The initial 24 bits (which is equal to the first 6 characters) provide information about the network card’s manufacturer. Manufacturers assign this part in order to give their devices exclusive identifiers.
- Device ID: These last 6 characters (or 24 bits) are unique to each device produced by the manufacturer, ensuring that each device has its own distinct address.
Function and Usage
If devices are connected to the same local network, they use MAC physical addresses to communicate with each other. For example, if you want to send a file from your laptop to your printer over Wi-Fi, your laptop uses the MAC address to ensure that the file is sent wirelessly directly to the printer (and not another laptop nearby).
Network equipment such as switches also use these addresses for efficient data routing purposes.
Permanent Nature
In contrast to IP addresses, which may vary according to the network or configuration, MAC addresses remain constant as they are embedded in hardware. This makes MAC addresses dependable for identifying devices on a network. Unless you deliberately modify it, your MAC address does not change; it always stays the same.
What is an IP Address?
Think of an IP (Internet Protocol) address as your device’s home address on a network or the internet. It’s a special set of numbers that identifies one particular device and helps it communicate with others over networks.
This is important for routing data correctly: if you want to visit a website or send information online, your IP address makes sure that data goes where it should.
Structure and Format
There are two versions of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6.
- IPv4: This is the common format – four numbers separated by periods, such as 196. 166. 1. 1. Each number can be from 0 to 255. This set of numbers gives each device on a network its own unique address.
- IPv6: Because the internet is expanding, it requires more IP addresses, which is why IPv6 was created. An IPv6 address consists of eight sets of digits, each separated by a colon, like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. With this format, there can be many unique IP addresses.
Function and Usage
Every networking device has its unique identification number known as an IP address that enables them to transmit data. Your device employs the IP address while attempting to join with the server which is hosting the website.
The information of the website is sent by the server to your IP address, so you can see it in your browser.
Dynamic vs. Static IP Addresses
- Dynamic IP Address: Dynamic host IP addresses are what most devices in a network get from a router or server and they may vary. It is a usual thing to find this kind of IP addressing in home and office networks.
- Static IP Address: Static IP addresses are necessary for certain devices such as servers and printers, which are required to maintain the same IP address. These are called static IP addresses and are set manually.
A practical example of these two would be the use of different type proxies.
- Mobile proxies (such as 3G, 4G connections) provide constant rotating IP address,
- Residential (and especially Dedicated, Static and ISP proxies) provide you with a constant IP, which can be a positive longevity factor for your business account efforts.
What are the Differences Between MAC Address and IP Address?
| Characteristic | MAC Address | IP Address |
| Full Form | Media Access Control Address | Internet Protocol Address |
| Structure | 48-bit address (6 bytes) in hexadecimal format | 32-bit (IPv4) or 128-bit (IPv6) in decimal/hex format |
| Function | Identifies device hardware | Identifies device’s network location |
| Layer | Data link layer (hardware) | Network layer (software) |
| Assignment | Assigned by NIC manufacturer | Assigned by Internet Service Provider (ISP) |
| Changeability | Permanent (unchangeable) | Temporary (can change over time or location) |
| Protocol Usage | Used by address resolution protocol ARP | Used by RARP protocol |
| Discovery | Not easily discoverable by unauthorized users | Discoverable by third parties |
| Data Forwarding | Required by switches | Required by routers |
| Address Format | 6 groups of 2 hexadecimal digits, e.g., 00:FF:FF:AB:BB:AA | IPv4: 192.168.1.1, IPv6: FFFF:F200:3204:0B00 |
| Class System | No classes | Classes A, B, C, D, E (IPv4) |
| Sharing | Not shared | Can be shared by multiple devices |
Device Tracking Through MAC and IP Addresses
Tracking devices through MAC and IP addresses is a common practice in both local and online networks, and understanding how this works can help you manage your privacy better.
Tracking Through MAC Addresses
A MAC address is a unique identifier assigned to the network hardware in your device, like your Wi-Fi card. It helps your device connect to a local network, like your home or office Wi-Fi. When you connect to a network, your MAC address is used to identify your device and keep track of its activity on that network.
For example, businesses with Wi-Fi might use MAC addresses to see how long customers stay in different parts of the store or how often they visit. While this can help businesses improve their services, it also means your device’s activity can be monitored.
On the flip side, one should remember that MAC addresses can also be hidden or tampered with. To enhance privacy, most of the new devices randomly generate MAC addresses while they are looking for network connections.
Tracking Through IP Addresses
IP addresses, unlike MAC addresses, are used to identify your device across the internet. When you visit a website or use an online service, your IP address helps route data to and from your device. Websites and online services use IP addresses to gather information like your general location and browsing habits.
To illustrate, your IP address can indicate the particular city or area where you are located; this may be employed by some sites to display local contents or advertisements. Additionally, IP addresses are recorded by websites in order to monitor how users interact with them.
Users can use tools like VPNs or proxies to hide or change their IP addresses, which helps protect their privacy and makes it harder for websites to track their activity.
Reasons to Change MAC Address vs IP Address
Changing your MAC or IP address can be driven by a variety of needs and concerns, from privacy to network management.
Here are some common reasons why individuals and organizations might choose to alter these identifiers:
1. Enhancing Privacy and Anonymity
One of the primary reasons for changing your MAC or IP address is to improve privacy and anonymity online. An IP address can be used to track your location and online activities. By regularly changing your IP address, or using a VPN to mask it, you can make it harder for websites and online services to build a profile of your browsing habits.
In the same manner, the MAC address that is unique for each device can serve as a means of following someone across different networks. It is advisable to change your MAC address from time to time to enhance your privacy, especially in environments where you connect to multiple public or semi-public networks.
2. Bypassing Network Restrictions and Blocks
Network administrators often use MAC and IP addresses work to implement access controls, such as restricting access to certain websites or services. If you find yourself blocked or restricted, changing your IP address can help you bypass these blocks.
For instance, if your IP address is blocked from accessing a particular website, obtaining a new IP address might grant you access.
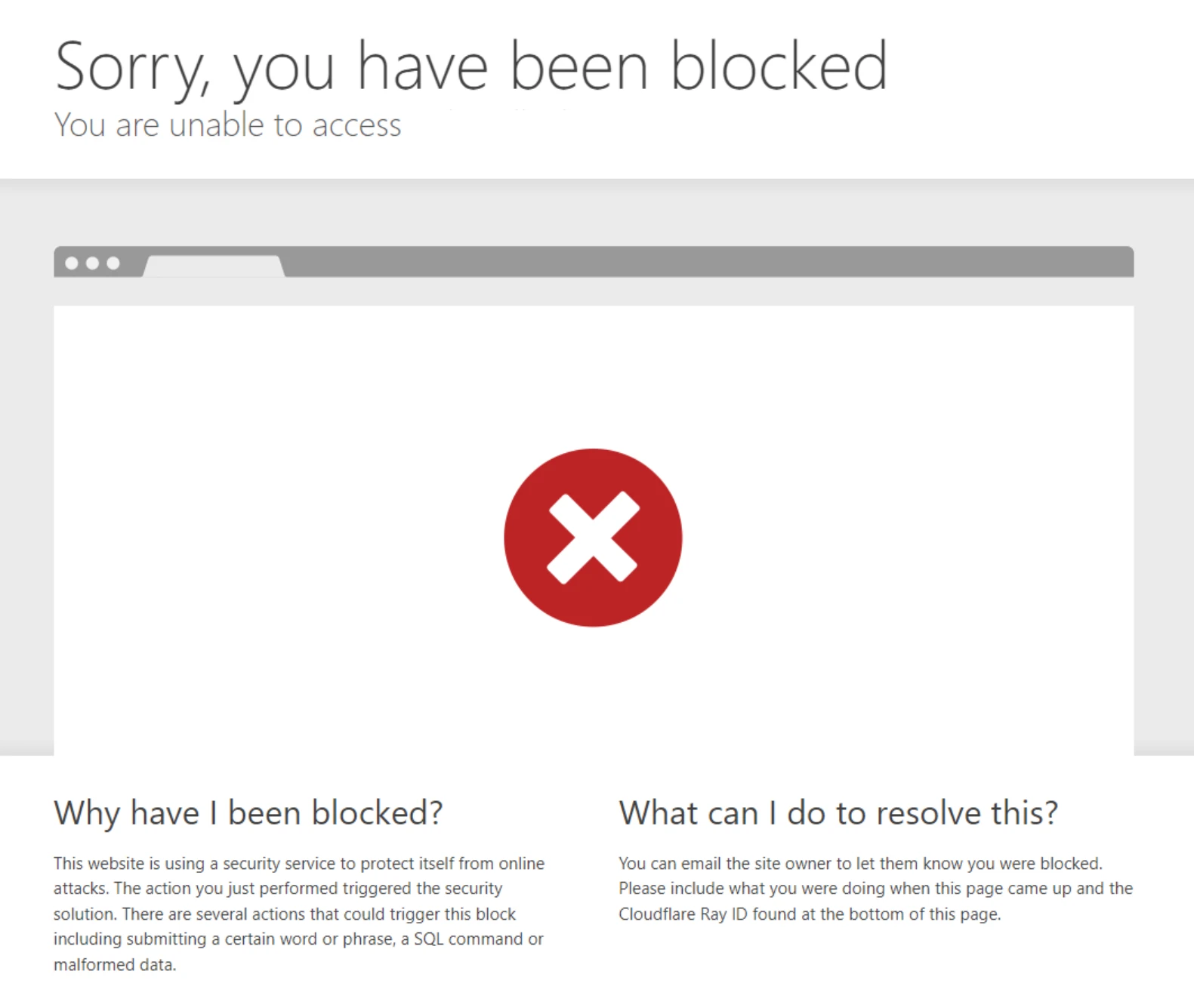
In some cases, changing your MAC address might also help if network restrictions are applied based on MAC address filtering. However, this approach is less common compared to IP address changes.
3. Resolving Network Conflicts
In networks where multiple devices share the same IP address, conflicts can arise, leading to connectivity issues. This is often a problem in smaller networks or during network configuration changes. By assigning new destination IP addresses to devices, you can resolve these conflicts and restore proper connectivity.
Similarly, if two devices on the same network accidentally have the same MAC address, it can cause issues with network communication. Changing the MAC address on one of the devices can resolve these conflicts.
4. Avoiding Targeted Attacks
Cybercriminals sometimes use MAC or IP addresses to target specific devices for attacks. By changing these identifiers, you can make it more challenging for attackers to target your device or track your online presence.
This is particularly relevant if you believe your device is being specifically targeted or if you are experiencing frequent cyber attacks.
5. Testing and Troubleshooting
For network administrators and IT professionals, changing MAC and IP addresses can be a part of testing and troubleshooting processes.
By altering these addresses, professionals can test network configurations, simulate different network conditions, and diagnose issues more effectively.
6. Improving Device Security
In some cases, changing your MAC address can enhance security by preventing unauthorized devices from connecting to your network.
If you suspect that your MAC address might have been compromised or is being spoofed, changing it can help protect your device from potential security threats.
Does a VPN Hide Your MAC Address? Why Some Sites and Social Networks See Through VPNs
Despite the protections a VPN provides, some sites and social networks can still track and identify network users. Here’s why:
Browser Fingerprinting
Websites can use advanced techniques like browser fingerprinting to collect various pieces of information about your device, browser settings, and behavior. This method can often distinguish users even if they are using a VPN.
Device Fingerprinting
Some sites and networks may use device fingerprinting techniques, which gather information about your device’s hardware, software, and configuration. This data can almost always bypass VPN protections.
Cookies and Tracking Scripts
Many websites use cookies and other tracking scripts to monitor user activity. Even with a VPN, these cookies can persist and be used to track you across sessions. You can also use special cookie management tools: see how to use cookie managers.
Login Information
If you log into a site or social network while connected to a VPN, the service may still link your activity to your account. This can reveal your identity regardless of the VPN.
IP Address Leaks
In some cases, VPNs may not fully mask your IP address due to issues like DNS leaks or WebRTC leaks, which can expose your real IP to websites.
Common Methods for Replacing MAC Address vs IP Address
Windows 11 and Windows 10
- Replacing IP Address: To change your IP address in Windows, you can either disconnect and reconnect to your network to get a new IP from your router or manually configure a new IP address with a control panel. After hitting the Windows key, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Change adapter options. Double click your network connection, select Properties, choose Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), and set a new IP address.
- Replacing MAC Address: To change your MAC address on Windows, open Device Manager, find your network adapter under Network adapters, right-click and select Properties. Go to the Advanced tab, find Network Address or Locally Administered Address, and set a new MAC address. Note that not all network adapters support MAC address changes.
macOS
- Replacing IP Address: On macOS, you can change your IP address by going to System Preferences > Network. Select your network connection, click Advanced, and go to the TCP/IP tab. Choose a new IP address or set it to use DHCP for automatic IP assignment.
- Replacing MAC Address: To change your MAC address on macOS, open Terminal and use the command prompt sudo ifconfig en0 ether xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx (replace en0 with your network interfaces and xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx with your desired MAC address). This change will be temporary and will revert after a restart.
iOS
- Replacing IP Address: On iOS devices, you can obtain a new IP address by going to Settings > Wi-Fi, selecting your network, and toggling the Auto-Join option off and on. For a more controlled approach, you can configure a static IP by tapping on the network, selecting Configure IP, and entering a new IP address.
- Replacing MAC Address: iOS devices use a feature called “private address” to frequently change the MAC address used when connecting to Wi-Fi networks. To enable this, go to Settings > Wi-Fi, tap the information icon next to your network, and toggle Private Address on.
Android
- Replacing IP Address: On Android, you can change your IP address by going to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi. Tap on your network, select Advanced, and choose IP settings to switch between DHCP and static IP configurations.
- Replacing MAC Address: Changing the MAC address on Android typically requires root access. For rooted devices, you can use third party apps to execute commands that change the MAC address.
Note: For non-rooted devices, you can only use random MAC addresses in Wi-Fi networks by enabling the MAC address randomization feature under Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Advanced > MAC address type.
The Modern Way Of Changing MAC and IP Safely: Antidetect Browsers
Antidetects are new generation privacy browsers, designed to completely stop sharing your information during your online sessions. They provide multiple browser profiles, each with a clean and real new device fingerprint – including both MAC and IP address, as well as about 50 other device parameters.
Most of these are commercial because they’re used in digital marketing a lot, however most have free plans for personal use. Antidetects also provide good proxy IP management features, which in total enables you to reach complete anonymity.
Using an antidetect browser (assuming you use a trusted one), you don’t need to bother about MAC or IP address replacement. Tools like GoLogin provide complete protection and hence are used a whole lot by digital marketers, as these work even on social media.
Let’s see how antidetects work using GoLogin as example.
How Does GoLogin Work?
GoLogin is one of the top tools on the market that helps protect your privacy by managing your complete device fingerprint + IP address and MAC address.
Total anonymity is reached not by masking or encrypting your device and IP, but rather providing new clean parameters of an authentic real device. You don’t have to guess between MAC address vs IP address anymore.
With Gologin’s antidetect technology, there is a close to zero chance of being traced on even most advanced websites, including even social and crypto platforms with extreme tracking.
In contrast to VPN (virtual private network) tools that encrypt your real parameters causing suspicion, GoLogin provides you with a new device fingerprint, MAC address and clean IP address from a proxy.
How GoLogin Is Used For Marketing Businesses
GoLogin and other antidetects are changing the game for many digital businesses, allowing for comfortable and safe social media use on a business scale.
Here’s how it’s used for Facebook and other social media:
If you run a business that needs anonymous surfing to protect your data from excessive device fingerprinting, website blocks and restrictions, GoLogin offers a reliable antidetect browser solution.
It will provide completely anonymous browsing that’s also helpful for marketing needs such as running multiple accounts with no restrictions.
Named Easiest to use antidetect browser according to G2 reviews, GoLogin is an essential tool for comprehensive protection against device fingerprinting, identity-based cyber attacks, MAC stealing and account loss.
Recap on MAC Address vs IP Address
- MAC addresses serve as permanent IDs for devices on a local area network. They are fixed and consist of 48 bits.
- IP addresses act as temporary identifiers for internet communication. They can be rotating or static depending on your internet connection type.
- Changing your MAC or IP address can help you bypass restrictions and improve security from tracking.
- Using VPNs can help enhance privacy, however it’s not effective as modern websites often use device fingerprinting.
- Tools like GoLogin antidetect browser are best for maintaining safety and integrity online, as they replace the whole device fingerprint including MAC and IP address.
GoLogin offers a free plan for personal use which is best for anonymity – try it out today!