Currently, people and companies are more worried about their online privacy than ever before. While surfing the internet, you may not realize that your Internet activities, settings of your device, and even installed fonts can be used to create a unique “fingerprint” that identifies you online. But what is browser fingerprinting, and should you care?
Websites and advertisers can monitor you through this technique called browser fingerprinting which does not require them to employ traditional tracking tools such as cookies.
What is Browser Fingerprinting?
Websites and advertisers use browser fingerprinting to get a lot of information about the user’s software, device, and browsing behavior which they then turn into a unique identifier or “fingerprint.”
Unlike traditional tracking methods like cookies that involve keeping records on a user’s device, browser fingerprinting does not need interaction with the user’s system.
Instead, it leverages the inherent characteristics of a user’s browser and device configuration, making it a more subtle and persistent form of tracking.
Which Data Is Collected?
Brace yourself, the list will be quite long. A sheer amount of data is collected in browser fingerprinting, consisting of:
- Browser and Version: The specific web browser you’re using (e.g., Chrome, Firefox) and its version.
- Operating System: Information about your operating system, such as Windows, macOS, or Linux.
- Screen Resolution and Color Depth: The dimensions and color capabilities of your display.
- Fonts: A list of fonts installed on your device, which can vary widely between users.
- Plugins and Extensions: Information about browser plugins and extensions, including their versions.
- Time Zone and Language: Your local time zone and preferred language settings.
- User-Agent String: An extra parameter that identifies the browser, operating system, and device type.
- Canvas Fingerprinting: The unique rendering of graphics by your browser’s HTML5 Canvas element.
- WebGL and Audio Context: Details about your graphics card and audio stack, as rendered by the browser.
- Cookies and Local Storage: The presence of cookies or data stored in the browser’s local storage.
If you’ve ever used targeted ads as an advertiser, you must have seen options like Target only Iphone 14 or MacOS users. Now that’s exactly how social platforms know how to target specific users – because all of the users share this information with them through browser fingerprinting.
Remember that major social media and marketplaces stay free because they mostly earn money selling your personal data to data brokers for targeted ads and marketing.
Browser Fingerprinting vs. Device Fingerprinting
- Browser fingerprinting targets the distinguishing features in the software environment.
- Device fingerprinting goes further to cover even hardware related data.
For example, a device fingerprint may capture unique hardware attributes like MAC address, CPU type or even the battery level. The combination of these two types of data – software and hardware – makes device fingerprinting even more precise and challenging to circumvent.
Browser fingerprinting is commonly employed in following users over a web session, whereas device fingerprinting may track them continuously on various networks for extended periods. Although both are effective for advertisers and analytics companies, they greatly violate the privacy of the users.
Examples of Browser Fingerprinting
When browser fingerprinting is happening, it is a smooth process that does not attract attention. It includes gathering and looking into many features taken from the connecting browser configuration then combining them together into a unique identifying hash.
It may incorporate scores of features that are specific to each particular kind of browser. Browser fingerprinting aims at developing an individualized user profile to control monitoring their activities on various websites or during different sessions.
While no single attribute stands out as more important than another in creating a unique fingerprint, certain characteristics are often more closely associated with fraudulent activities.
Here are some examples of data points within a browser fingerprint that are commonly linked to fraud detection:
1. Installed Plugins
If a person has some special plugins in the browser that are meant for improving privacy level and preventing fingerprinting, it can indicate a higher risk of fraudulent behavior. Such instruments are widely applied by people who want to keep their tracks unknown, therefore they can cause suspicion from security systems.
2. Unexpected Browser Version Age
Outdated browser versions that have already received security updates may sometimes be used by internet criminals to take advantage of known vulnerabilities. As such, using an extremely out of date browser is suspicious and associated with potential fraud.
3. Uncommon Screen Resolutions
Screen resolutions that appear unusually small or outdated might suggest the use of multiple accounts on a single device. To do this, several devices are emulated on a single physical screen with the help of some Virtual Machine (VM) environment. Also, the use of VM, which is another feature that may be known through browser fingerprinting, could imply an effort to mask fraudulent behavior.
4. Particularly Unusual Configurations
Unusual configurations like using non-standard plugins, old browser versions and rare screen resolutions may be indicative of a bot attack. If this is the case, one browser in one device could control many profiles at the same time. Some tools allow for the customization of rules to assign higher risk scores to these unusual configurations, helping to identify and prevent fraud more effectively.
How Does Browser Fingerprinting Work?
To create a browser fingerprint, information is gathered from various points in your browser and device. This information is then used to create a unique identifier for you, which can be referred to as a “fingerprint” and can separate one person from the others online.
It is different from cookies and other conventional tracking technologies that depend on saving details on the user’s computer since it does not require one to store any data on the hard drive. Below is an explanation of this process:
1. Data Collection
Upon visiting a site, your browser is asked by the server to provide different kinds of information. The asking of this information is what leads to the gathering of certain data points such as:
- HTTP Headers: This data is important for displaying web pages properly, but can also be used to identify a person. Examples of such data are: your browser type, version, operating system, and the language settings your browser uses.
- JavaScript and APIs: JavaScript enables websites to collect in-depth details about your browser and device. To illustrate, through JavaScript one can determine your screen resolution, installed fonts, time zone, and even identify if your browser has some particular plugins or extensions installed. On top of that, web APIs may gather even more specific information like the type of GPU in your device via WebGL or how a browser displays content through certain HTML5 features.
- Cookies and Local Storage: Even though cookies and data stored in local storage are not the most important way of creating a fingerprint, they can still help in this process by providing more information for identification, such as tracking past visits or storing user preferences.
2. Data Analysis and Hashing
After gathering all the necessary data points, they are scrutinized and then merged to form what is known as hash. This hash is a simple but distinct representation of the way your browser has been set up. With an increase in the number of data points collected, the hash becomes more unique, making it highly unlikely that another user will have the same fingerprint.
Take, for instance, a browser that is recognized as being “Chrome 116 on Windows 11 with a screen resolution of 1920 by 1080 pixels, color depth of 32-bit, specific installed fonts, and certain browser extensions.” The combination of all these characteristics results in a distinct identifier which may track your activities across other websites and browsing sessions.
3. Tracking and Profiling
The development of a distinct fingerprint enables monitoring of your activities on various websites even in the absence of cookies or other forms of persistent storage. In essence, clearing your cookies, surfing incognito or changing networks will not help because your fingerprint still stays there to keep on tracking you.
Browser fingerprinting techniques are used by most websites to monitor users without them knowing. This kind of monitoring may cause one to be blocked severally in social sites or have problems when trying to access some internet services. Because your digital fingerprint remains consistent across sessions and sites, platforms can recognize and enforce restrictions or bans based on your unique profile.
4. Continuous Updating
Your browser fingerprint is not constant; it changes with time due to updates on the browser, addition of new applications and changing the system configurations. These systems have been made in such a way that they can identify any changes made and then adjust the fingerprint.
By continuously updating the fingerprint with these modifications, your profile remains accurate and up-to-date, making fingerprinting a highly effective and resilient tracking method.
5. Fraud Detection and Security Applications
Apart from advertising, browser fingerprinting serves as a tool for enhancing security as well as preventing fraud. To give an example, banking and finance systems may rely on fingerprinting to confirm that a given transaction is taking place from a familiar device.
In cases there’s an attempt to login using a device with a different fingerprint, then it would mean that the transaction is not secure and additional verification will be required.
Top Browser Fingerprinting Techniques
To collect a detailed profile of a user’s device and browser configuration, browser fingerprinting uses complex methods that gather individual data points. It is hard for one to conceal their digital identity as every method focuses on a certain area of the operating environment.
Some examples of the top fingerprinting techniques employed nowadays are:
Canvas Fingerprinting
The HTML5 Canvas element is used by canvas fingerprinting to draw graphics or text on your browser. Websites can create a unique “canvas fingerprint” by taking advantage of the fact that when your browser is told to render text or images, it does so slightly differently depending on factors related to your hardware and software (such as graphics cards, drivers, and other installed applications).
Although these differences may seem insignificant, they serve as important indicators that help distinguish one user from another.
A script is operated by the website on your browser instructing it to display some text or an image through the Canvas API. After that, the hash function converts the final image/text into a unique identifier.
Canvas fingerprints are very distinct due to the fact that even the smallest changes in the rendering process can be used for tracking effectively across sessions and websites.
WebGL Fingerprinting
Just like canvas fingerprinting, WebGL fingerprinting also captures unique images of your device. The WebGL (Web Graphics Library) is a JavaScript API that enables the rendering of 3D graphics in a web browser. The way these graphics are rendered may slightly vary across different devices and browsers due to graphics hardware, driver versions, as well as operating systems.
The WebGL script on a website is responsible for generating a 3D scene. By looking at how the scene appears, one can gather information on the individual’s GPU, graphic drivers as well as some other related hardware and software settings.
WebGL fingerprints are very distinct due to the combination of various hardware and software factors which further individualizes a person’s fingerprint.
Media Device Fingerprinting
Information is collected by the fingerprinting of media devices which are linked to your PC; this may include microphones, cameras as well as speakers. It is possible to identify some characteristics of your computer set up by looking at how these devices are configured and what drivers they use.
JavaScript on websites can be utilized to ask about your browser information concerning what type of connected media devices you have, their characteristics, as well as the make and model among other details. All this data is part of a unique fingerprint.
The technique adds unique data points to the fingerprint, which improves its accuracy, given that media devices are usually customized and differ among individuals.
Mobile Device Fingerprinting
When doing mobile device fingerprinting, one considers unique properties of mobile gadgets such as screen size, touch input, battery status as well as sensor data (like accelerometers and gyroscopes). In addition, mobile browsers have unique configurations as well as user-agent strings that are different from those of desktop browsers, creating more fingerprinting opportunities.
Data on mobile hardware and software, such as operating system, browser, display size etc., are gathered by websites. This results in a unique digital fingerprint for every mobile phone.
Due to the fact that mobile devices are highly customized, with configurations that differ from one user to the other, mobile device fingerprint is particularly precise.
TLS Fingerprinting
TLS fingerprinting is the examination of Transport Layer Security parameters. It is a process that allows a secure link between the user’s browser and the server. Analysis entails looking at how different kinds of equipment, operating systems and browsers create unique fingerprints by slightly varying their negotiation of TLS connections.
The TLS handshake process involves the exchange of some information between the client (your browser) and server such as what protocols they support, their encryption algorithms among others. This is what is referred to as a TLS fingerprint; it comprises a unique combination of these parameters.
Given that TLS handshake is integral in ensuring secure data exchange, this fingerprinting method can still monitor users over encrypted connections when other forms of monitoring fail.
Font Fingerprinting
Font fingerprinting involves looking at the kind of fonts that have been installed in your computer system, which can vary widely between users. This may be used as a unique identifier: a list of fonts, their rendering specifics and availability.
When you visit a website, it scans the fonts that are currently in use on your device. Typically, this is achieved by trying different fonts to see what happens with the text. The presence or absence of certain fonts, along with how they display, contributes to your fingerprint.
Because font libraries can be different depending on the operating system, installed software and user preferences, fonts can be used reliably to identify users.
Audio Fingerprinting
The analysis of audio fingerprints includes studying the way in which sound is handled and produced by a particular device. Audio signals are processed differently by various devices or even browsers because of differences in hardware, drivers and audio software that introduce slight variations.
By utilizing the Web Audio API, a website can produce a sound, analyze the way your browser processes it and receives it back. The specific distortions or characteristics of the processed sound create an audio fingerprint.
Audio fingerprints are usually distinct and hard to hide because the audio processing pipeline differs across devices and configurations.
How Browser Fingerprinting Can Help Detect Fraud?
In the battle against online fraud, browser fingerprinting has been a powerful and effective tool. Most banking, crypto and social media platform websites and systems (including Paypal, Facebook, Amazon, Google, LinkedIn and even Reddit) implement some level of browser fingerprinting.
When information is gathered from the browser and the device of any user, it could be used to easily point out any anomaly which may signify some form of potential fraud and restrict user from the system.
This is where fraud detection heavily relies on browser fingerprinting:
Identifying Fraudulent Behavior
In order to detect and take appropriate action against these kinds of users without inconveniencing the majority’s user experience, it is important to be keen on some techniques which aid in detecting browser fingerprinting and other online fraud activities.
- Spotting Suspicious Users: A distinct user profile is formulated using information about the browser and device which is then later analyzed for any anomalies e.g. unusual attempts to login; on such occasions, it can be flagged for further investigation.
- Adding Extra Security: If an account raises suspicion, extra security measures like added verification steps can be taken without inconveniencing genuine users. In this way, the sight is kept safe but still easy to use.
Bypassing Traditional Concealment Techniques
Despite fraudsters’ attempts to conceal their activities such as turning off cookies, utilizing VPNs or using incognito mode, browser fingerprinting can be used to monitor them.
- Working Without Cookies: Cookies may be removed or blocked with private browsing, unlike fingerprints which are based on the persistent characteristics of a browser or device. Therefore, it is possible to continue tracking even after clearing the cookies.
- Avoiding IP Limitations: Fingerprinting provides a more dependable means of monitoring and identifying users because it is not dependent on IP address which can be hidden using VPN or proxy IPs.
Preventing Account Takeovers
Browser fingerprinting is one way that can be used to prevent account takeovers (social accounts included), which are occasions where intruders get into user accounts without permission.
- Adding Extra Checks: In case a login attempt is made using a strange or questionable fingerprint, the system may demand for more proof apart from the usual one like a security code. By doing this, it becomes difficult for hackers to gain entry into people’s accounts.
- Detecting Patterns: Browser fingerprints work by revealing when multiple accounts are accessed from the same device, a common sign of attempted takeovers. This allows for early intervention to protect user accounts.
Protecting Against Phishing Scams
Phishing scams trick users into revealing their login information. Browser fingerprinting can help protect against these scams by:
- Detecting New Devices: If a login attempt comes from a new or unusual device, additional verification can be required. This helps ensure that the attempt is legitimate and not the result of a phishing scam.
- Blocking Suspicious Activity: Fingerprints linked to repeated suspicious activities can be blocked, which reduces the risk of unauthorized access from phishing.
Combating Brute Force and Bot Attacks
Brute force attacks and bots try to break into accounts by rapidly guessing passwords. Browser fingerprinting helps by:
- Recognizing Patterns: It can detect when many failed login attempts come from the same fingerprint, a sign of automated attacks. This allows the system to block suspicious activity before it causes problems.
- Taking Action Early: By monitoring fingerprints continuously, websites can spot and stop attacks early, reducing the impact on users and the site.
Tools and Strategies to Protect Yourself
Although browser fingerprinting is effective in monitoring users online, there are ways of ensuring that your privacy is kept safe. If you know how your internet movements get tracked, then you will be able to reduce your digital footprint and keep controlling where your data goes.
So, how do you prevent browser fingerprinting?
Regularly Clear Cookies and Cache
Even though browser fingerprinting is not dependent on cookies, erasing cookies and cache every now and then can also minimize tracking.
To create a detailed profile, most tracking techniques combine the use of cookies, IP tracking and fingerprinting; therefore, deleting your cookies may interrupt this process.
There are special tools made for cookie management.
Avoid Unnecessary Plugins and Extensions
Your digital fingerprint can be made unique by every plugin or extension that you install. You can lower the distinctiveness of your fingerprint by limiting the number of plugins and using trusted ones only.
Use a Browser Fingerprint Checker
Tools like iphey.com offer a reliable browser fingerprint checker that allows you to see exactly what data points websites are collecting about you. By using this service, you can get a detailed report of your browser’s fingerprint, including information such as your browser type, version, operating system, screen resolution, and more.
- How It Helps: Knowing what data is exposed helps you understand your vulnerability to tracking and allows you to take specific actions to protect yourself and avoid identity theft.
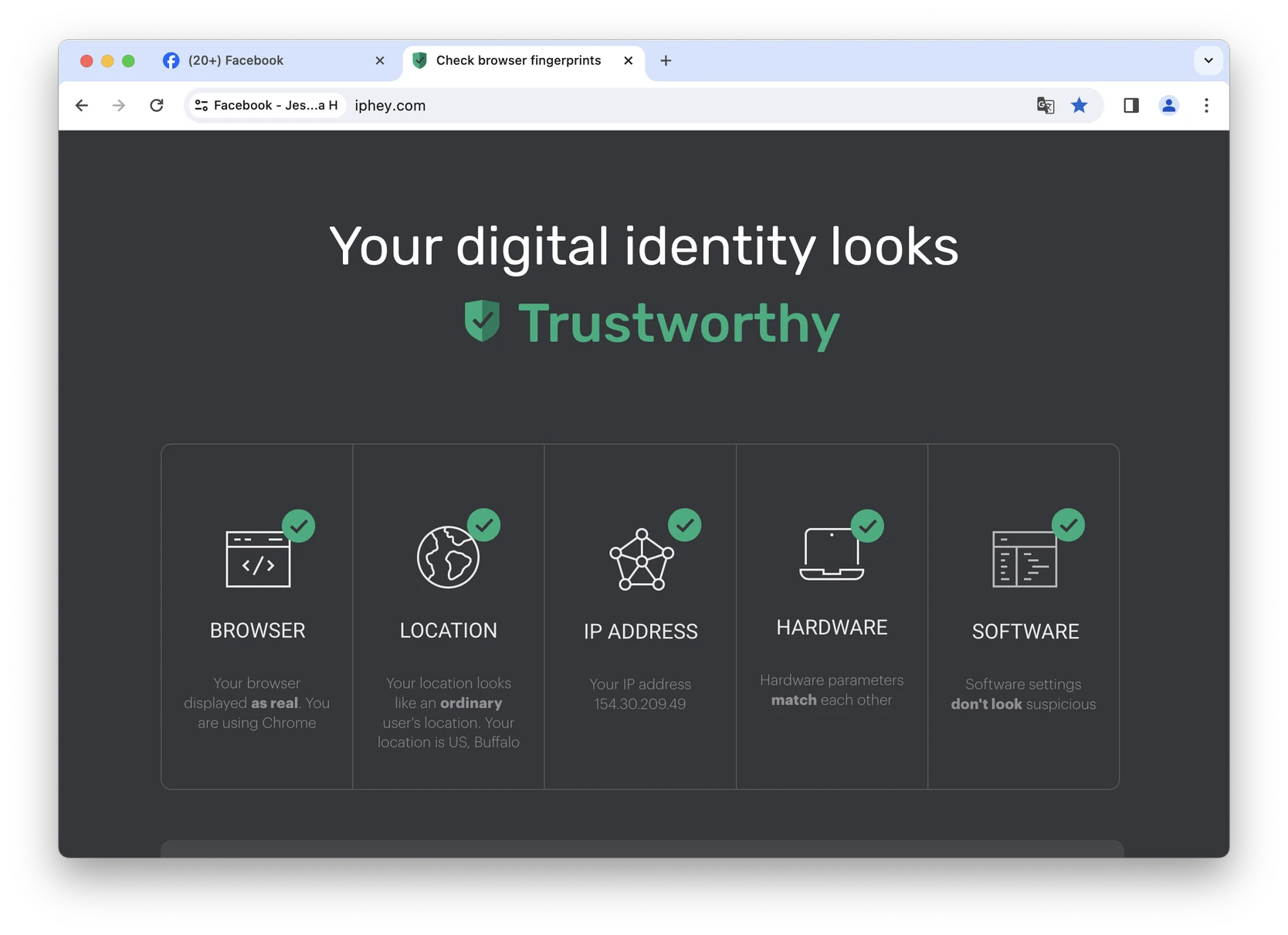 Iphey is just one of the browser fingerprint checkers – visit any of them to see the sheer amount of data websites see about you and your device.
Iphey is just one of the browser fingerprint checkers – visit any of them to see the sheer amount of data websites see about you and your device.
Use An Antidetect Browser
A basic incognito mode in Chrome will only keep you logged out of websites, but it still collects all info about you for Google.
Most common privacy browsers will mask or randomize your browser fingerprint at best. This can be helpful, but on some websites it will trigger anti-bot protection – for example, on most social media websites are able to see you’re using a randomized fingerprint.
However, there are also new generation privacy browsers designed to completely stop sharing your information during your online sessions, called antidetect browsers. They provide multiple browser profiles, each with a clean and real browser fingerprint. Most of them are commercial because they’re used in digital marketing a lot, however most have free plans for personal use.
Antidetects also provide good proxy IP management features, which in total enables you to reach complete anonymity.
We’ll show an example of an antidetect below.
What is GoLogin Antidetect Browser?
GoLogin is one of the top tools on the market that helps protect your privacy by managing your complete device fingerprint + IP address.
With Gologin’s antidetect technology, you can surf the net with total anonymity – there is a close to zero chance of being traced on even most advanced websites, including even social and crypto platforms with extreme tracking.
 Originally a privacy tool, GoLogin is widely used by digital businesses and marketers as a unified account control panel and a tool to safely cooperate with remote employees.
Originally a privacy tool, GoLogin is widely used by digital businesses and marketers as a unified account control panel and a tool to safely cooperate with remote employees.
In contrast to VPN (virtual private network) tools that encrypt your real parameters, GoLogin provides you with a new device fingerprint and clean IP address.
It’s specifically designed to enhance your privacy by preventing tracking and monitoring in the first place, not by masking or selling your information.
The antidetect technology of GoLogin provides increased anonymity and better management of users’ footprints as compared to the regular VPNs and proxies that are known today.
How GoLogin Is Used For Marketing Businesses
For solopreneurs, SMBs and scaling agencies, this is a game changer because it allows for comfortable and safe social media use on a business scale.
Here’s how it’s used for Facebook and other social media:
If you run a business that needs anonymous surfing to protect your digital footprint from excessive tracking, website blocks and restrictions, GoLogin offers a reliable antidetect browser solution. It will provide completely anonymous browsing that’s also helpful for marketing needs such as running multiple accounts with no restrictions.
Named Easiest to use antidetect browser according to G2 reviews, GoLogin is an essential tool for comprehensive protection against identity-based cyber attacks and account loss.
Recap on What Is Browser Fingerprinting
- A browser fingerprint refers to the various personal data that is collected about you while using the internet through your browser and device.
- Browser fingerprinting has its positive use cases (like banking operations safety), but it’s often used to track users for commercial reasons.
- There are several ways to manage and minimize tracking, including understanding your online behavior, reviewing privacy settings, opting out of cookie collection and using antidetect browsers.
- Tools like GoLogin antidetect browser offer real anonymity and protection against browser fingerprinting, compared to incognito mode, VPNs and proxies.
GoLogin offers a free plan for personal use which is best for anonymity – try it out today!
Read other posts about fingerprinting:
What Is Device Fingerprinting, And Should You Care?
What Is a Digital Footprint?
The Ultimate Anti Fingerprint Browser List
Device Fingerprinting Explainer
WebGl and Canvas Fingerprinting Explainer
Understanding Canvas Fingerprinting