If a company keeps accounting information, customer base, employee profiles, or corporate secrets, this data must be protected. And an ordinary person will not want other people to receive his personal data. That’s why information security is important. In this article, we will tell you what it is and what kind of data it protects.
- Why information security?
- What Does Information Security Guard?
- Main Types of Confidential Information
- Types of Information
- Main Types of Confidential Information
- Briefly About Information Security
- TOP 5 Information Security Threats
- Malware
- Phishing
- Ransomware
- Internal threats
- 1Cloud Vulnerability
- Conclusion

Why information security?
Information security is various measures to protect information from unauthorized persons. In the pre-digital era, people locked important documents in safes, hired security guards, and encrypted their messages on paper to protect data.
Today, digital information is more often protected. Still, the measures are essentially the same: information security specialists create protected spaces (virtual “safes”), install security software like antivirus (“hire security guards”) and use cryptographic methods to encrypt digital information.
However, digital information also needs to be protected not only virtually but also physically. Antivirus will not help if an outsider steals the server itself with important data. Therefore, they are placed in guarded premises.
What Does Information Security Guard?
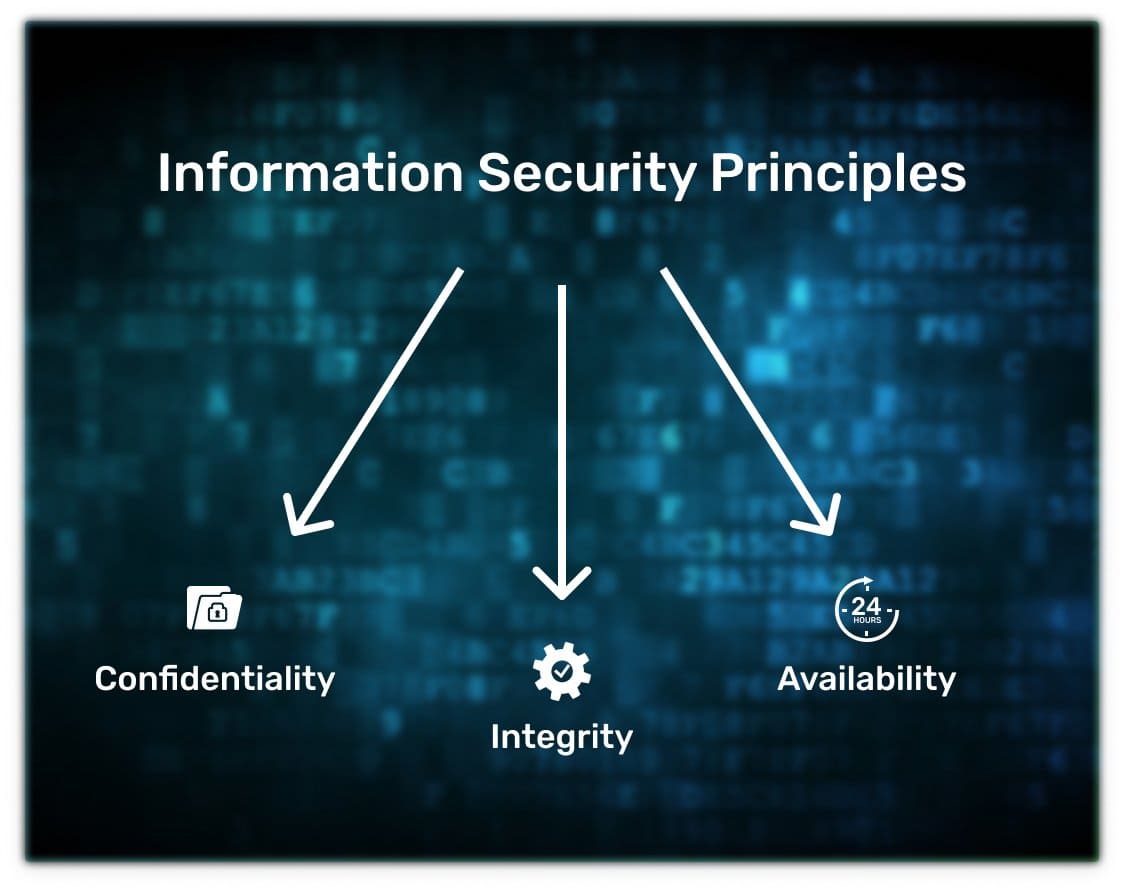
It is responsible for three things: confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. In the information security concept, they are called information security principles:
- Confidentiality means that only those who have the right to do so have access to information. For example, only you know your email password, and only you can read your emails. If someone finds out the password or otherwise gains access to the mailbox, confidentiality will be violated.
- Integrity means that information is preserved in full and is not changed without the owner’s knowledge. For example, your email contains letters. If an attacker deletes some or changes the text of individual emails, this will violate the integrity.
- Availability means that whoever has the right to access information can obtain it. For example, you can log into your email at any time. If hackers attack the servers, mail will be unavailable, and this will compromise availability.
Main Types of Confidential Information
It is responsible for three things: confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. In the information security concept, they are called information security principles:
Types of Information
Information can be public and confidential. Anyone has access to the public, while only individuals can access the confidential one.
It may seem that there is no need to protect public information. But only the principle of confidentiality does not apply to publicly available information – it must remain integral and accessible. Therefore, information cybersecurity also deals with publicly available information.
For example, let’s think about an online store. Product cards, blog articles, seller contacts – all this crucial information is publicly available, and anyone can view it. But the online store still needs to be protected so that no one disrupts its work (for example, not change important information in the product cards or “drop” its site).
The main task of information security in IT and not only is the protection of confidential information. If someone gains access to it, it will lead to unpleasant consequences:
- Theft of money
- Loss of company profits
- Violation of constitutional human rights
- Other troubles
If everything is clear with publicly available information, it is worth talking about confidential information separately since it has several varieties.

Main Types of Confidential Information
Personal Information. Information about a specific person: full name, passport data, phone number, physiological characteristics, marital status, and other data. Anyone who works with personal data is obliged to protect it and not transfer it to third parties. Information about customers and employees refers to personal data.
Trade secret. Internal information about the company’s work: technologies, management methods, customer base. If this data becomes known to outsiders, the company may lose profits. The company itself decides what is considered a trade secret and what is exposed to the public. Moreover, not all information can be a trade secret – for example, the founders of the legal entity or working conditions cannot be hidden.
Professional secret.It includes medical, notarial, lawyers, and other types of secrets related to professional activities. Several laws are connected with it at once
Official secret.Information that is known to individual services, for example, the tax or registry office. Government agencies usually store this data. They are responsible for protecting it and only provide it upon request.
State secret.State secret.
If your company stores personal data, commercial or professional secrets, then this data must be protected specially. It is necessary to restrict access to it for unauthorized persons:
- set access levels and passwords;
- install security software;
- configure encryption.
Briefly About Information Security
- Information security is responsible for protecting data and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Confidentiality means that only those who have the right to do so have access to the data.
- Integrity means that data is stored unchanged and remains valid.
- Availability means that the person who has the right to access information can get it.
- Information security protects both confidential and public data. It ensures integrity and availability to the public. While confidential, it also provides the required level of secrecy.
- Confidential information includes personal data, commercial, professional, official, and state secrets.

TOP 5 Information Security Threats
Knowledge of the potential threats and the security vulnerabilities that these threats typically exploit is essential to select the most appropriate security controls.
“Threat” is understood as a potential opportunity to violate information security in one way or another. An attempt to implement a threat is called an “attack”, and the one who implements this attempt is called an “attacker.” Most often, the threat is a consequence of vulnerabilities in the protection of information systems. Let’s consider the most common threats to which modern information systems are exposed.
Malware
Malware is malicious software that is specially designed to harm the system. Malware is used to classify malicious programs into a group of programs that are much more dangerous than single viruses. Malware is classified according to how it is launched, how it works, and its distribution.
Malware’s action strategy differs from a virus in that it causes non-standard system behavior and can remain unnoticed for a long time. Such a program can be created to intentionally harm the system and create an environment suitable for the reproduction of other computer viruses or Trojans that steal information from the computer.
To launch, Malware disguises itself by attaching itself to interesting content such as pictures, videos, animated GIFs, and often hides in videos and adult pictures.
Malware cannot get into the computer without the user’s help. To infiltrate the system, Malware has to use any means to fool its victims into running it on their PC.
The main recommendation, which guarantees more or less secure work, includes mandatory antivirus scanning of each new file or attachment to an email before opening or launching it.

Phishing
Phishing is one of the most common types of online fraud, where the goal is to obtain identification data. The actions of fraudsters can lead to consequences of varying severity: from an innocent banner on a personal computer to the loss of company content without the possibility of restoring it. The main purpose of phishing is to steal something valuable, use it, compromise or bring down someone’s business. What phishers usually target:
- personal data, including passport;
- all kinds of logins and passwords;
- access codes;
- data for entering personal accounts;
- details of bank cards or accounts;
- personal correspondence;
- service information;
- database;
- information that is a trade secret, etc.
First of all, experts advise service users to learn how to recognize phishing on their own. Check the authenticity of the service messages first. At the same time, any letters that do not contain any specific personal information should cause suspicion.
Also, we recommend you enter an organization’s URL by yourself in the address bar instead of using any hyperlinks. A link can also be sent to you by a friend or acquaintance whose account has been hacked. If a letter or link has made you suspicious, it is better not to follow it.

Ransomware
Ransomware is created by highly professional programmers. Such a program can penetrate the victim’s device via an attachment file in an email message. mail or through a browser if you visit a site infected with this type of malware. It can also penetrate the user’s device from the local network. How to recognize ransomware?
Ransomware infection can be seen with the naked eye, as in most cases the device is completely locked and you simply cannot use it. And how to remove it?
Use the ransomware removal tool of your antivirus solution, which should detect and remove any type of ransomware from your device. Then protect yourself from ransomware:
- Make sure all software, including the operating system, browser and other plugins and toolbars, is up to date.
- Also make sure to install the latest updates for your antivirus and firewall solutions.
- Using a modern antivirus solution with built-in protection against all types of viruses is the most effective way to prevent, detect and remove ransomware from your computer.

Internal threats
Most information security incidents are related to the impact of internal threats. Leaks and thefts of information, trade secrets, and personal data of customers, damage to the information system are associated, as a rule, with the actions of employees of this organization. In the classification of internal threats, there are two broad groups: threats committed for selfish or other malicious reasons, and threats committed through negligence or technical incompetence.
So, the crimes of employees who can harm the safety of the organization’s intellectual and commercial property (they are called “insiders”) can be divided into the categories of malicious insider and unintentional insider. A malicious insider can be:
- employees who harbor a grudge against the employing company (“offended”);
- employees seeking to earn extra money at the expense of the employing company;
- injected and recruited insiders.
A large proportion of all information security incidents are the result of unintentional employee actions. There are many opportunities for such information leaks: from data entry errors when working with local networks or the Internet to the loss of a storage medium (laptop, USB drive, optical disk), from sending data over insecure communication channels unintentionally downloading viruses from entertainment websites.
Defending against internal threats requires an integrated approach. It is expressed in the development of appropriate information security policies, the hiring of employees responsible for information security, document flow control, control and monitoring of users, the introduction of advanced authentication mechanisms.

Cloud Vulnerability
The following classes of threats should be distinguished when using cloud computing:
- Client attacks. This type of attack has been practiced in the web environment, but it is also relevant for the cloud, as clients connect to the cloud, usually using a browser. It includes such attacks as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), hijacking web sessions, stealing passwords, ‘man in the middle,’ and others.
- Virtualization threats. Since the platform for cloud components has traditionally been virtualized environments, attacks on the virtualization system also threaten the entire cloud. This type of threat is unique to cloud computing.
- Hypervisor attacks. A virtual system’s critical element is the hypervisor, which provides the sharing of physical computer resources between virtual machines. Interfering with the hypervisor’s operation can lead to the fact that one virtual machine can access the memory and resources, intercept its network traffic, take away its physical resources, and even wholly displace the virtual machine from the server.
So far, all the threats listed above are purely hypothetical since there is practically no information about real attacks of this type. Simultaneously, when virtualization and cloud become popular enough, all these types of attacks can be quite real. Therefore, they should be borne in mind at the stage of designing cloud systems and at the same time developing technical solutions in the field of in-the-cloud security.
Also read:
TOP 5 Best Ways to Hide Your Identity Online
Conclusion
Information security measures in the enterprise and private life must be developed and implemented continuously.
The solution to this issue must be approached comprehensively and with third-party specialists and special programs (like anti detect browsers). Only this approach will prevent data leakage and not deal with its consequences. We hope that now you know “why is information security important?”.


